
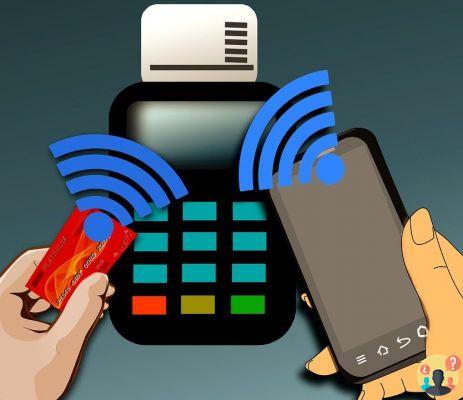
Close and interactive: devices connected via NFC they cannot be more than ten centimeters away from each other and they begin to exchange data almost instantly.
The wireless connectivity of NFC - Near Field Communication is in fact, literally, "narrow field", a proximity wifi. But it is also an evolution of RFID – Radio Frequency Identification, identification on radio frequencies, which allows you to verify connected devices very quickly.
From verification to data exchange, the transition is almost immediate: a feature that makes NFC technology one of the most used for digital payments, especially if contactless.
Index of topics
What is NFC used for on phones
NFC replacement phone it is used to exchange data between two devices at a short distance without using cables connection. For example, to carry out a payment transaction via app, between a smartphone and a POS or between two smartphones.


The NFC wireless connectivity system is based on radio waves: more precisely, it is an evolution of RFID, radio frequency identification.
La RFID need to authenticate and track objects and people: in the business field, labels are placed on products to follow the flow of logistics. But it's a kind of one-way communication: labels are "passive" because they do not in turn query the reader/writer.
La NFC has inherited the transmission methods and the distinction between the "active" and "passive" communication: the devices “passive”, like small transmitters, they don't process the information received and can not link to other passive components. The devices “active”, come smartphone o POS, send and receive data, communicating with each other.
In the event that both devices are "active", however, they will alternate their electromagnetic fields according to whether they have to "ask" (activation) or "answer" (deactivation).

The NFC standard has three modes of operation: card emulation – Card Emulation Mode; reading/writing – Reader/Writer Mode; the Peer-to-Peer.
In Card Emulation Mode or card emulation, the NFC device, such as one smartphone, simulates the behavior of a payment card.
In fact, there are more and more payment cards that have a passive NFC chip, a tag/transponder that is read by active devices such as contactless POS. The smartphone therefore, in combination with the digital payment apps, "makes itself read" by the POS enabled to carry out the transaction.
In the mode of read / write o Reader/Writer, lo smartphone NFC-enabled becomes an active device that reads the information in the chips-passive transponders (e.g. stickers on labels).
In the mode peer-to-peer, which allows person-to-person payments, i two devices (e.g. two phones) connected via NFC alternately communicate with each other.

How to check if the NFC on our phone works
L’NFC works if on the smartphone the appropriate chip has been integrated, standard or through special SIM or microSD.
From Android, you can manually check if the NFC on your smartphone is active; on iOS it is always on tramite Apple Pay.
To check on Android, just go to “Settings” and type “NFC” in the search bar at the top. Or, still from "Settings" check the "Wireless and networks" or "Connections" sections: once you find "NFC and contactless payments", enable the option "On".
NFC and Bluetooth: similarities and differences
Both NFC and Bluetooth are wireless connectivity systems.
But while the NFC is close range, maximum 10 centimeters, the Bluetooth it works even 10 meters away between devices.

La frequency through NFC is 13,56 MHz, the one via Bluetooth 2,45 GHz: Bluetooth therefore has a much higher frequency but also more crowded with devices (e.g. wi-fi). L'NFC consume less.
La maximum data rate via NFC is 424 kbit / s, respect to 2 Mbit / s of Bluetooth 5: NFC is Than we slower in the transfer. Ma connects faster, because it does not have to activate the manual pairing of devices as in Bluetooth,
NFC is ideal for devices that need to connect quickly and exchange little data, as in the case of theand digital transactions.
Il Bluetooth and instead recommended for large data exchanges and for connections of IT and IoT peripherals. There are also integrated solutions such as NFC headphones that connect in close range but transmit music files via Bluetooth.
Close-range communication in digital transactions increases safety, as it prevents unwanted connections and interference.
L’NFC it is extremely fast, both in the identification of the devices and in the authorization of the transaction: the evolution of RFID makes authentication and association between devices automatic, identifying the radio frequency in proximity. Just bring them together.

The combination with digital payment apps makes the smartphone a mobile wallet, with all the conveniences (but not the weight) of a physical wallet plus the ability to view and manage your expenses with a click.















![[Solved] Android App Won't Open Problem](/images/posts/a150cb8db0eb50df4b79257485e3c04c-0.jpg)